Fleas are small, blood-sucking insects that primarily affect pets, especially cats and dogs. However, fleas can also bite humans, causing irritation, itching, and discomfort.

While fleas are often associated with pets, they can infest homes and gardens, making them a potential issue for humans, especially in regions with high flea populations.
What Are Fleas?
Fleas are tiny, wingless insects belonging to the order Siphonaptera. Adult fleas have specialized body structures that allow them to jump long distances, which is why they can easily transfer between animals and humans. Fleas feed on the blood of mammals, including humans, and their bites can cause discomfort and itching. The most common flea species that affect humans are the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis) and the dog flea (Ctenocephalides canis).
Fleas are primarily found in areas where animals live or frequent, such as pet beds, carpets, and furniture. They are also commonly found in homes with rodents or other wildlife, making them a widespread problem.
Symptoms of Flea Bites on Humans
Flea bites on humans can cause a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild irritation to more severe reactions, depending on the person’s sensitivity. Some of the common symptoms of flea bites on humans include:
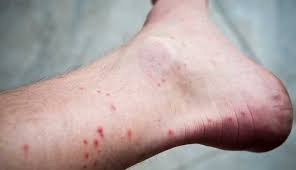
- Itching: The most noticeable symptom of a flea bite is intense itching. This occurs as a result of the flea’s saliva, which contains proteins that trigger an allergic reaction in humans. The itching can be severe and persistent, especially if the bites are scratched.
- Red, Raised Bumps: Flea bites typically appear as small, red, raised bumps on the skin. These bumps are often clustered together in groups or form a line, as fleas tend to bite multiple times in a concentrated area.
- Swelling: In some cases, flea bites can cause mild swelling around the affected area. This can make the bite appear larger and more inflamed.
- Skin Irritation: Flea bites can cause skin irritation, which can become even more pronounced if the bites are scratched, potentially leading to an infection.
- Rashes: Prolonged exposure to flea bites or excessive scratching may result in the development of rashes. In rare cases, flea bites can trigger more severe allergic reactions, including hives.
- Infection: If flea bites are scratched excessively, bacteria from the skin can enter the wound, leading to infections. This can cause increased redness, pain, and the formation of pus around the bite.
- Flea Allergy Dermatitis (FAD): Some people are highly sensitive to flea bites and may develop a condition known as flea allergy dermatitis (FAD). FAD can cause severe itching, inflammation, and scabbing, and in some cases, it may lead to chronic skin problems.
READ ALSO: Is Cheese Safe for Cats? The Surprising Truth
Treatment for Fleas on Humans
The treatment for flea bites on humans primarily involves managing the symptoms and reducing the risk of further exposure to fleas. Here are several steps you can take to alleviate the discomfort caused by flea bites:
1. Clean the Bites
- Gently wash the affected area with soap and water to remove any dirt or bacteria. This helps reduce the risk of infection and soothes the skin.
- Avoid scrubbing the bites, as this can exacerbate irritation and increase the risk of infection.
2. Use Anti-Itch Creams
- Over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams or calamine lotion can help relieve itching and reduce inflammation. Apply a small amount to the flea bites to soothe the skin.
- Antihistamine creams or gels containing diphenhydramine can also provide relief for allergic reactions caused by flea saliva.
3. Apply Cold Compresses
- A cold compress can reduce swelling and numb the area, providing immediate relief from itching and discomfort. Apply a cool, damp cloth to the bites for 10-15 minutes at a time.
4. Take Oral Antihistamines
- Over-the-counter antihistamines such as loratadine (Claritin) or cetirizine (Zyrtec) can help control itching and swelling caused by flea bites. These medications work by blocking histamines, which are responsible for allergic reactions.
5. Use Topical Antibiotics (If Infected)
- If the bites become infected, apply a topical antibiotic ointment such as Neosporin to the affected area. This can help prevent further infection and promote healing.
6. Avoid Scratching
- Although flea bites can be intensely itchy, try not to scratch them. Scratching can introduce bacteria and lead to infection, as well as worsen the irritation and delay healing.
7. Consult a Doctor
- If the flea bites become infected, or if you experience severe allergic reactions such as difficulty breathing, swelling, or dizziness, seek medical attention immediately. In some cases, a doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics or corticosteroid creams to manage symptoms.
How to Prevent Fleas on Humans
While treating flea bites is important, preventing fleas from infesting your home and biting you in the first place is the best way to avoid the discomfort and potential health risks associated with fleas. Here are several steps you can take to prevent fleas from biting humans:
1. Treat Pets for Fleas
- Fleas are often transmitted to humans through pets, so the most effective way to prevent fleas in your home is by treating your pets with flea prevention products. There are various types of flea treatments available, including oral medications, topical treatments, and flea collars. Regular flea treatments will help keep your pets flea-free and reduce the risk of infestation.
2. Vacuum Regularly
- Fleas and their eggs can hide in carpets, rugs, and upholstered furniture. Regular vacuuming can help remove fleas, eggs, and larvae from your home. Focus on areas where pets spend a lot of time, such as pet beds and furniture.
3. Wash Bedding and Linens
- Wash your pet’s bedding, your bedding, and any linens that may have come into contact with fleas. Use hot water and dry them on high heat to kill any fleas, larvae, or eggs that might be present.
4. Flea-Repelling Plants
- Certain plants, such as lavender, rosemary, and eucalyptus, are known to repel fleas. Consider planting these around your yard or using essential oils to keep fleas at bay.
5. Treat Your Home for Fleas
- If you suspect a flea infestation in your home, treat the environment with flea sprays or foggers. These products can help kill adult fleas and larvae, reducing the risk of future infestations. Always follow the instructions on the product to ensure safe application.
6. Limit Exposure to Wild Animals
- Fleas can be transmitted from wild animals, such as rodents, raccoons, and squirrels. Avoid areas where these animals are present, and take precautions if you live in an area prone to rodent or wildlife infestations.
7. Use Flea-Repellent Clothing
- When spending time in areas where fleas are prevalent, such as wooded areas or homes with pets, wear long sleeves, long pants, and socks to reduce the risk of flea bites. You can also apply insect repellent to exposed skin and clothing to keep fleas away.
FAQs
Can fleas live on humans?
- Fleas prefer to live on animals, as they require the warmth and fur of their host to survive. While fleas can bite humans, they typically don’t live on human skin or hair for extended periods.
How do I know if I have fleas in my home?
- Signs of a flea infestation include seeing adult fleas jumping around, noticing small black or dark brown specks (flea dirt) on furniture or bedding, and observing frequent scratching in your pets. If you find these signs, it’s important to treat your home and pets promptly.
Are flea bites dangerous?
- In most cases, flea bites are not dangerous but can be very irritating. However, if the bites become infected or cause an allergic reaction, complications can arise. In rare cases, fleas can transmit diseases such as plague or typhus, though this is not common.
Can I get fleas from my pet?
- Yes, fleas are commonly transferred to humans through pets. Fleas can jump from your pet to your skin, and if not controlled, they can bite and cause discomfort.
How long do flea bites last?
- Flea bites typically last a few hours to a few days. The itching and swelling should subside after a few days, but it may persist if the bites are scratched or become infected.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.